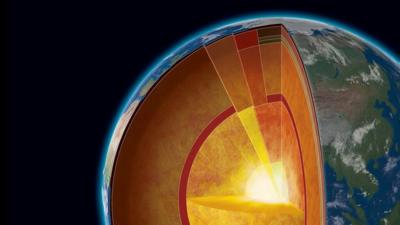
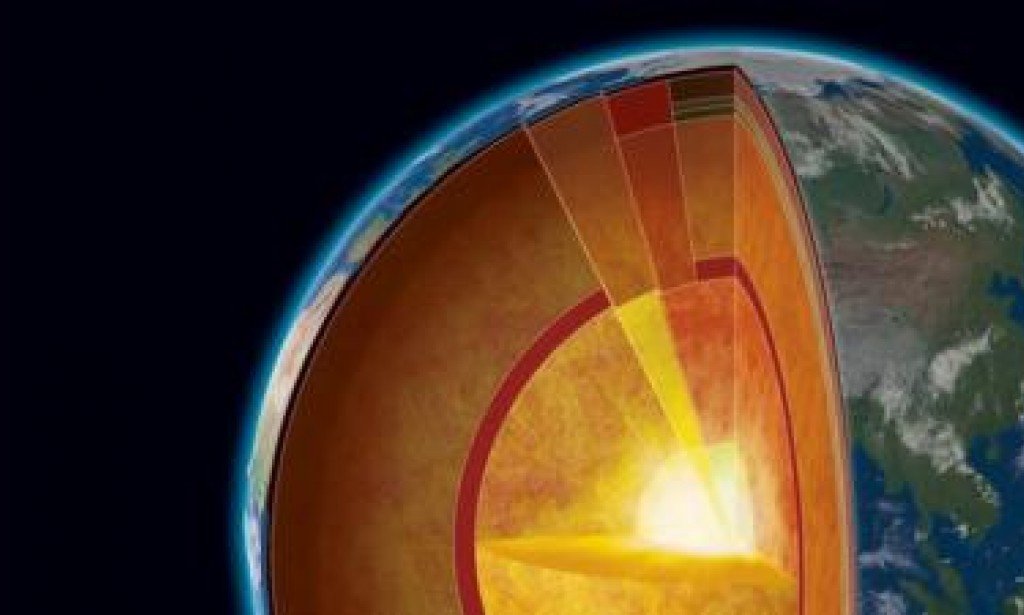
A team of Chinese scientists verified that the Earth's inner core has shifted its rotation axis after examining seismic wave motion and recent alterations.
In a study that was published on Monday in the scholarly journal Nature Geoscience, the researchers noted that altering the rotation of the Earth's deep core would decrease the duration of days by a tiny fraction of a second throughout the year.
They also noted that, in line with "Wall Street Journal" reports, this will likewise have a negligible impact on the Earth's magnetic field.
earthquakes and tremors
The study's assistant researcher and seismology specialist from the University of Peking, Xiadong Song, responded by saying that although in theory this issue has persisted for a long time, there are signs that it just started a few decades ago.
Song pointed out that examining the rotational movement of the Earth's inner core can help scientists better understand how the various layers of the planet interact with one another. The Earth's inner core rotates because of the magnetic field produced by the outer liquid layer.
The Earth's inner core's rotation ceased between 2009 and 2020, and they hypothesised that it had reversed its rotation, saying: "We have these earthquakes that occur in the same locations... we were We subject the Earth to a tomogram." He also studied the seismic waves produced by earthquakes and compared them to similar tremors in the 1960s.
another viewpoint
University of Southern California professor John Vidal, who was not engaged in the current study, has a different viewpoint. He thinks that although the researchers' observations of changes are reasonable, the particular reason why they are occurring is unknown, and that there may be another way to look at the data they provided.
He emphasised that although the analysis and theory of the study are superior to what is currently available, there are other hypotheses that could contradict them.
Other experts, according to Vidal, believe that the Earth's inner core rotates more often than during the seventy years of the research was conducted and that either the inner core stopped revolving between 2001 and 2003 or that its rotational movement was never halted. She changed the way she moved.
The fact that the Earth's inner core is made of iron and nickel and is separated from the solid component of the planet by a liquid outer layer helps to alter its velocity in a way that differs from the motion of the entire planet.
Why is Earth suddenly moving less quickly?
Since the 1960s, when operators of radio telescopes all over the world started to develop ways to simultaneously analyse cosmic phenomena like quasars, we have had highly accurate estimations of the Earth's rate of rotation.
When these estimates and an atomic clock were contrasted, it became clear that the length of the day had been getting shorter recently.
A shocking discovery is made after we take the tide- and season-related fluctuations in rotation speed into account.
The shortest day on Earth will occur on June 29 of 2022, however the long-term trend seems to have shifted from shortening to lengthening after 2020.
There has never been a transformation like this during the past 50 years.
It's unknown why this change took place. Even if back-to-back La Nia events have occurred in the past, weather system alterations might be to blame. There is a probability that the ice sheets' consistent pace of melting has increased even if it hasn't altered much in recent years.
Could it have something to do with the large-scale volcanic eruption in Tonga that released a lot of water into the atmosphere? Most likely not, given that it occurred in January 2022.
The recent, puzzling change in the speed of the planet's rotation has been attributed by scientists to the "Chandler wobble," a little deviation in the Earth's rotation axis with a period of around 430 days.
Recent radio telescope measurements show that the wobble has diminished, and there may be a connection between the two.
The third scenario we deem plausible is that nothing specific has changed on or around Earth.
It might just be that long-term tidal impacts and periodic processes are combining to momentarily change the Earth's rotational speed.
يجب عليك تسجيل الدخول لتستطيع كتابة تعليق